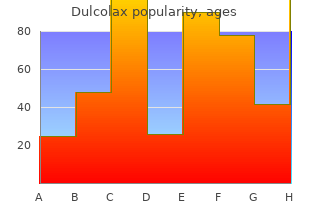
Dulcolax
"Discount dulcolax 5mg with mastercard, symptoms zinc poisoning."
By: Stephen Joseph Balevic, MD
- Assistant Professor of Pediatrics
- Assistant Professor of Medicine
- Member of the Duke Clinical Research Institute

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/stephen-joseph-balevic-md
The findings of this study showed that symptoms diabetes buy dulcolax mastercard, the vast majority of patients in the experimental and control subjects had experienced normal affected limb regarding color symptoms 7 weeks pregnancy dulcolax 5mg free shipping, temperature medications you can buy in mexico buy 5 mg dulcolax with amex, sensation, peripheral pulse and capillary refill. This finding was supported by Kaushal(2015) who reported that, post cardiac catheterization the affected limb must be warm, with normalperipheral pulse and color,as well as without any abnormal sensation [37] such as numbness. Regarding back pain the findings showed that, patients in the control group experienced more back pain compared to the experimental. This could be due to the prolonged bed rest without any change in the patients position. This shows that the more the patients rest in the supine position after femoral diagnostic [36,38] cardiac catheterization, the more intense back pain they would experience. Moreover,The results illustrated that, change patients position after femoral diagnostic cardiac catheterization was associated with a lower level of back pain intensity. This is in line with findings of Adaryaniet al (2009)and Abdollahi et al (2015) who reported that patients may be able to safely change their position in bed earlier in the postcoronary angiography, additionally changing position in bedand using a supportive pillow during the early hours after cardiac catheterization can effectively minimize back painand hemodynamic instability without increasing vascular [35,8] complications. This also in congruence with Sabzaligol et al (2010)andThangkratok (2016) who reported that back pain intensity was lower in the intervention group than the control one after 6 and 24 hours of [39,40] catheterization (P<0. The results showed that,all studied patients in both groups have no incidence of vascular complications including bleeding and hematoma after transfemoral diagnostic cardiac catheterization. As for satisfaction with theprocedure among patients in the two study groups, the present study has also demonstrated statistically significant differences. The findings have elucidated that patients satisfaction was lowest in the control group, and higher in the experimental group. This possibly could be due to the fact that, changing position in bed is frequently associated with patients comfort and decreasedintensity of back pain which helped to increase patient satisfaction level. This result was in line with a study conducted byAdaryani et al (2009) and Mohammady et al (2014)who ascertained that, patients in the experimental group had signi? Furthermore, changing patients position after cardiac catheterization are associated with increasing comfort and satisfaction levels without increasing the amount of [35,42] bleeding and hematoma. Conclusions Based on the findings of the current study, it can be concluded that, changing patients position in the bed by using supportive devices after transfemoral cardiac catheterization was safe and associated with a lower level of back pain intensity and improving patient satisfaction with noeffects on vascular complications (bleeding &hematoma ). Recommendations Establishing a standardized protocol for best positioning after transfemoral diagnostic cardiac catheterization. Efficacy of noninvasive cardiac imaging tests in diagnosis and management of stable coronary artery disease. Non Invasive Diagnostic Testing for Coronary Artery Disease in the Hypertensive Patient: Potential Advantages of a Risk Estimation-Based Algorithm. Effect of Positioning and Early Ambulation on Coronary Angiography Complications: a Randomized Clinical Trial. Ansen J,Femoral Artery Access?Poised for a Comeback:2016, available at:. Invasive imaging :cardiac cathterization and angiograph right heart catheterization: indicationsand interpretation. Grymuza M, Rajpold K, Jankiewicz S, Siniawski A, GrygierM, Mitkowski P Oleksy M, Lesiak M,KubzdelaT and Araszkiewicz A. Right heart catheterization procedures in patients with suspicion of pulmonary hypertension experiences of a tertiary center. An evaluation of peripheral vascular access site complications following coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention. Early sheath removal and ambulation in patients submitted to percutaneous coronary intervention: A randomised clinical trial. The effect of changes in patients body position on the back pain intensity and hemodynamic status during and after radiofrequency catheter ablation of cardiac dysrhythmias. Determining Best Nursing Practice: Effectiveness of Three Groin Compression Methods Following Cardiac Catheterization. Effect of Early Ambulation; Three versus Five hours after Transfemoral diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization: A randomized clinical One-arm Study.
Choice of instrument may be influenced by whether shortand medium- symptoms lyme disease purchase discount dulcolax online, or longer-term outcomes are the focus of investigation treatment kidney cancer symptoms generic dulcolax 5 mg with amex. If shortand medium-term outcomes are the main object of attention symptoms 0f low sodium discount 5 mg dulcolax free shipping, one of these surgery-specific measures could be the instrument of choice. The Duke Activity Status Index has considerable merit as a measure of cardiac patients capacity to engage in activities which are important to their QoL. Recommendations Based on this appraisal, the following instruments were recommended for consideration by a multidisciplinary panel (see Appendix D): 1. Table i: Psychometric and operational criteria 0 not reported (no evaluation completed)? Evaluation evidence available indicating poor performance of instrument + Some limited evidence in favour ++ Good evidence in favour +++ Excellent evidence in favour 37 Table ii: Appraisal criteria Appraisal component Definition/test Criteria for acceptability Reliability Test-retest reliability the stability of a measuring instrument Test-retest reliability correlations over time; assessed by administering the for summary scores 0. Expert being measured opinion and literature review Patients involved in the development stage and item generation Construct validity Evidence that the scale is correlated with High correlations between the scale other measures of the same or similar and relevant constructs preferably constructs in the hypothesised direction; based on a priori hypothesis with assessed on the basis of correlations predicted strength of correlation between the measure and other similar measures the ability of the scale to differentiate Statistically significant differences known-groups; assessed by comparing between known groups and/or a scores for sub-groups who are expected to difference of expected magnitude differ on the construct being measured (e. No summary score Frequency of Angina (2) Treatment Satisfaction (4) Disease Perception (3) Symptoms of Illness Score No. Interpretability] Scores
Our gray literature scan identified 12 scientific meeting abstracts that presented data on 104-115 11 studies not described in the published reports medicine natural purchase line dulcolax. These abstracts medications ending in ine buy dulcolax with a mastercard, which are summarized in Table 15 symptoms wheat allergy generic 5mg dulcolax amex, report data on 923 patients who underwent percutaneous heart valve replacement. Insufficient evidence was reported in the abstracts to make it possible to determine with confidence how many patients may be represented in more than one abstract, or in both an abstract and a fully published report. Data presented in abstract form at scientific meetings but not yet published in peer-reviewed journals are not included in this information synthesis for the following reasons: (1) meeting abstracts usually contain insufficient information to create sufficiently detailed evidence tables; (2) data presented at scientific meetings often differ from those that later appear in published reports, thereby putting into question the accuracy of the data presented in the abstracts; and (3) information presented at meetings is often derived from a subset of patients whose data have undergone only preliminary analysis. We describe the results from the abstracts we identified briefly in a separate section, below. We identified seven manufacturers of percutaneous heart valves through the published, peer-reviewed medical literature. The first 42 published report of percutaneous valve replacement in an adult involved a valve that was initially manufactured by Percutaneous Heart Valve, Inc. The device is referred to as ?Percutaneous Heart Valve in the initial published studies. Subsequently, the same device was referred to as the Cribier-Edwards valve in published reports. Reports in the non-peer-reviewed literature describe the Ascendra Aortic Heart Valve Replacement System as the Cribier-Edwards valve for use in transapical, rather than transfemoral, delivery. The second valve to appear in the published literature is the CoreValve ReValving System. The first generation was delivered via a femoral artery approach using a 25 French (Fr) catheter. We identified 22 reports, describing 21studies, that reported on a total of 424 unique patients who underwent percutaneous heart 74,77-97 valve replacement with a CoreValve device. We identified a single published report for each of the five additional percutaneous heart valve manufacturers, plus one case report in which the names of the valve and manufacturer 103 were not reported. A case report of the Paniagua Heart Valve, manufactured by Endoluminal 98 Technology Research, was published in 2005. Case reports of the Lotus Valve (Sadra 99 100 Medical) and the Melody Valve (Medtronic) were published in 2008. A case series that reported on the initial experience of the first 15 patients who received a Direct Flow Medical valve (Direct Flow Medical, Inc. In 2009, a case report was published that involved the Ventor Embracer valve 102 manufactured by Ventor Technologies. Thirty-five of the published reports were case reports, and 27 were case series, the latter representing a total of 822 patients. One study described the procedure and reported clinical outcomes on five patients who underwent a valvein-valve procedure, whereby a CoreValve Revalving device was implanted within a previously 90 implanted prosthetic heart valve in the aortic position. The controls were matched for sex, aortic annulus diameter, left ventricular ejection fraction, body surface area, and body mass index. Interpretation of these findings is complicated, however, by the many potential biases inherent to indirect comparisons between two or more patient populations whose clinical characteristics are significantly different between groups. Five reports described an antegrade approach via the femoral vein, 32 described a retrograde approach via the femoral artery, and 17 described a transapical approach, representing 37, 578, and 223 patients, respectively. Only 12 of the reports described the setting in which the procedure took place (e. Successful implantation of a heart valve percutaneously was achieved in 92 percent of cases. All but seven included followup data 30 days after the procedure or until death of the patient. Eleven reports (18 percent) provided followup data 1 or more years after the procedure. One reported on implantation of a prosthetic valve in the pulmonic position in a 100 young adult with congenital heart disease, and one reported on implantation in the mitral valve 76 position in an 80-year-old male with mitral stenosis. The remaining studies were conducted in patients with severe aortic stenosis who were considered to be at high surgical risk for conventional aortic replacement surgery (n = 854 patients). A small minority of patients had undergone heart valve replacement prior to undergoing percutaneous heart valve replacement. In nearly all patients, successful implantation of a prosthetic heart valve resulted in significant improvement in both valve area and either mean or peak pressure gradient across the replaced valve. Mild to moderate (Grade 1 or 2) paravalvular leaks were reported after the procedure in the majority of patients.
Cheap 5mg dulcolax amex. Prevent swine flu | പന്നിപ്പനി തടയാനുള്ള മാർഗ്ഗങ്ങൾ | Ethnic Health Court.